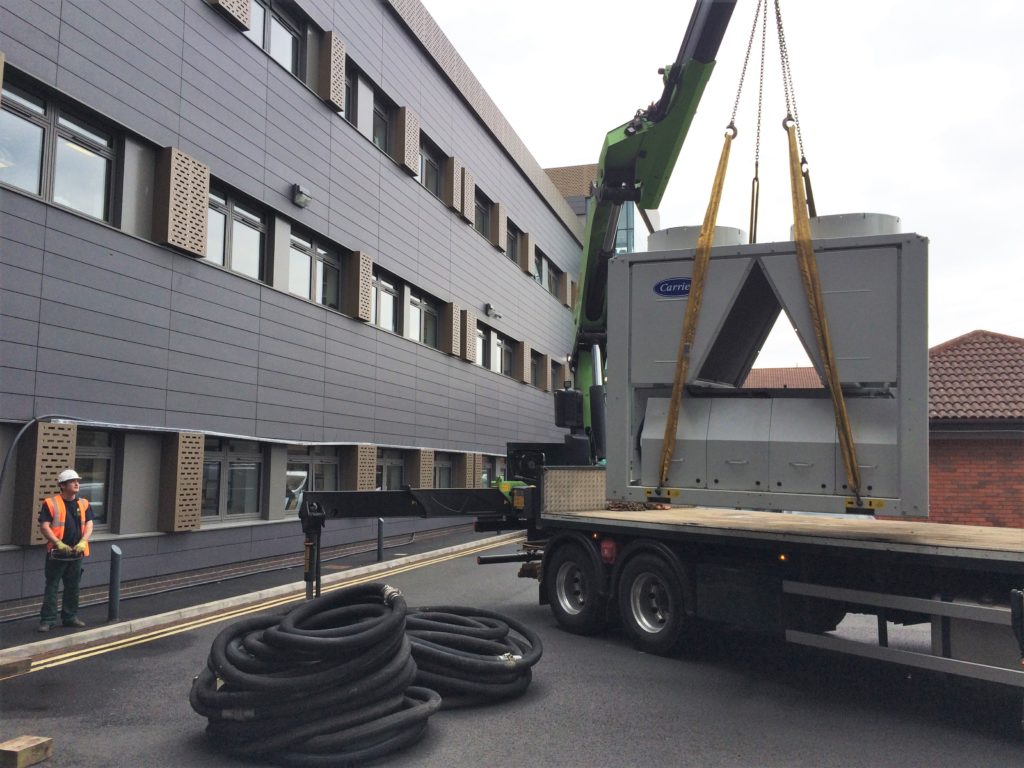
Heating system load testing is a process that applies thermal cooling to a heat generation system to validate the operational capacity. It is particularly useful for renewable decarbonised district heating systems requiring certification.
What are the Typical Processes used for Heat Load Testing?
The two main processes used for heating system load testing are;
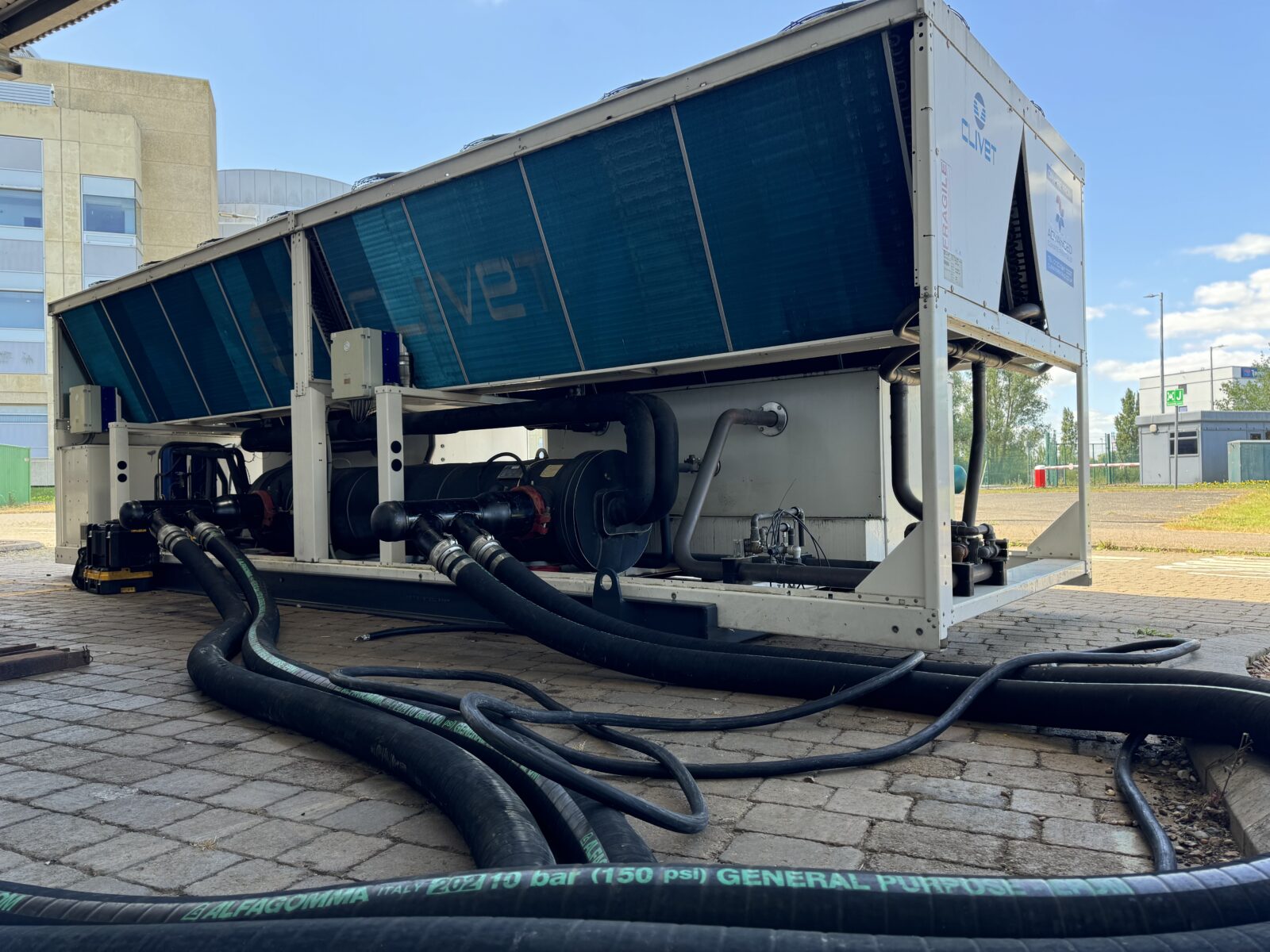
- Direct water to air systems which circulate the heating system water through finned tubed radiators, and using fans force air across the surface to remove heat from the water and dispel to atmosphere. These systems are very effective in lower temperature ambient conditions where there is a large difference between the air and fluid temperatures.
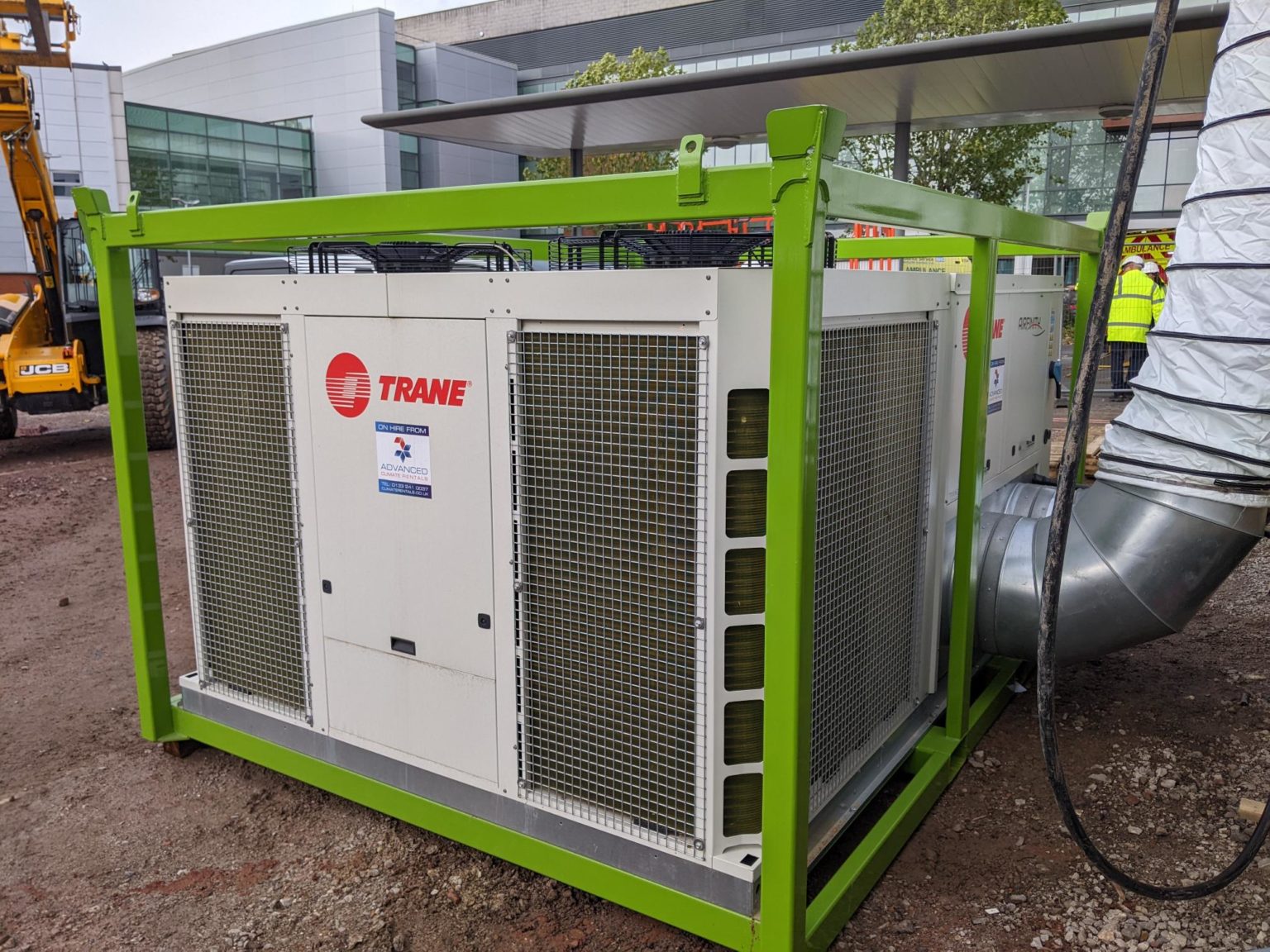
- Active refrigeration systems such as water chillers use a vapour compression system to move energy from the water and then to atmosphere. However, they are not suited to working with the higher temperatures of heating systems which means they are generally used with plate heat exchangers for separation .
Advantages/ disadvantages of using direct air to water systems for heat load testing;
- Advantages; High efficiency in certain conditions/ simple to use and operate.
- Disadvantages; Changing capacity to remove heat which is dependant on ambient conditions.
Advantages/ disadvantages of using active refrigeration systems for heat load testing;
Advantages; Provides a consistent capacity for heat removal in typical ambient conditions.
Disadvantages; Less efficient/ more complicated to set-up with more component parts and involved control strategy.